 Species Factsheets
Species Factsheets
Penstemon canescens
Gray Beardtongue
State Status: N
PBS Status: Tenatively Undetermined (TU)
Federal Status:
Global Rank: G4
![]() rank interpretation
rank interpretation
State Rank: S3
Did You Know?
The common name of beard tongue comes from the tuft of hair found on the stamen of the speices.
Description
Gray beardtongue (Penstemon canescens) is a perennial, hairy-stemmed herb from 40-80cm in height. The leaves are oppositely arranged, hairy, toothed on the margin, and at least the upper pairs of leaves lack distinct leaf stalks. The flowers are pale purplish and appear in late May and early June. The flowers have a two-lipped appearance, and an open throat that allows the entrance of pollinating insects. The name “beardtongue” refers to a sterile stamen that is covered with hairs. The fruit is a many-seeded capsule.
Rank Justification
Vulnerable in the nation or state due to a restricted range, relatively few populations (often 80 or fewer), recent and widespread declines, or other factors making it vulnerable to extirpation.
PABS
The PA Biological Survey considers gray beardtongue to be a species of special concern, based on the relatively few occurrences that have been confirmed and the limited range in the state. It has been assigned a rarity status of Undetermined, meaning that more information is needed before a more definitive rarity status can be designated.
Habitat
The species grows in open woods, woodland borders, banks, cliffs, and rocky slopes, particularly on shale substrate.
Survey Dates
Flowers May - July; fruits July - August
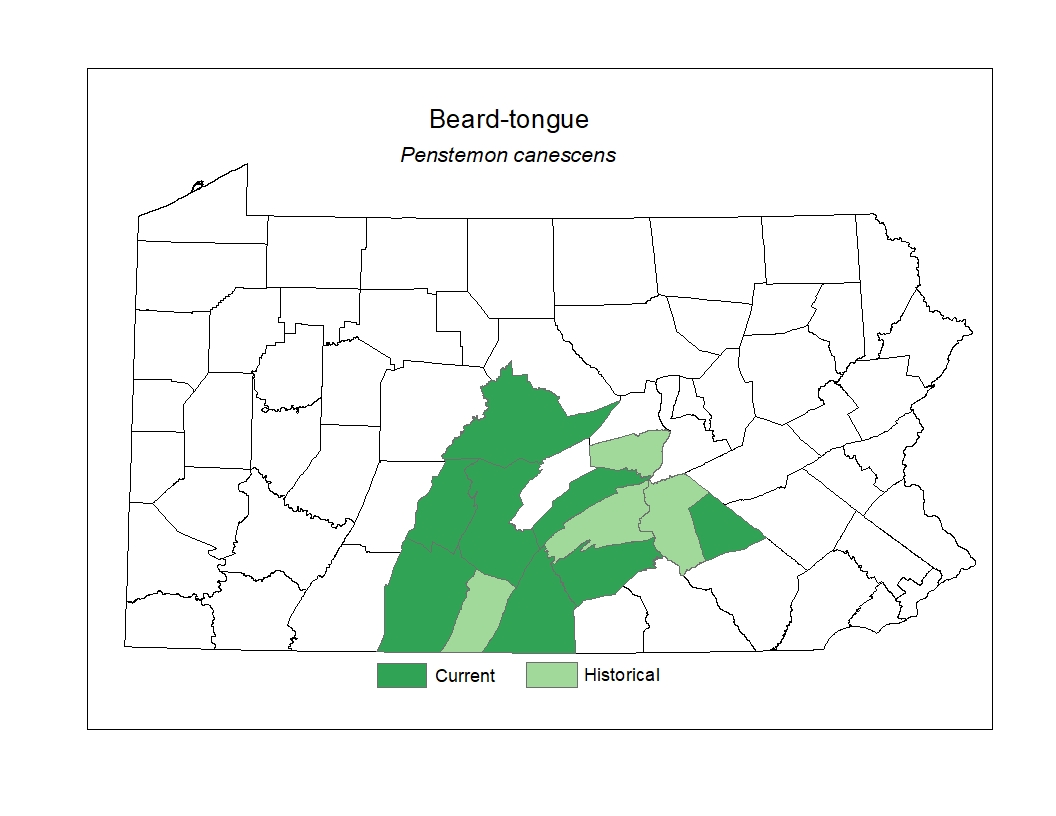
Distribution
In Pennsylvania, most of the known occurrences are located in the south-central counties.
Management
More field surveys are needed to determine the range, abundance, and ecological requirements of the gray beardtongue before a more definitive conservation status, if needed, can be assigned.
Conservation Status Map
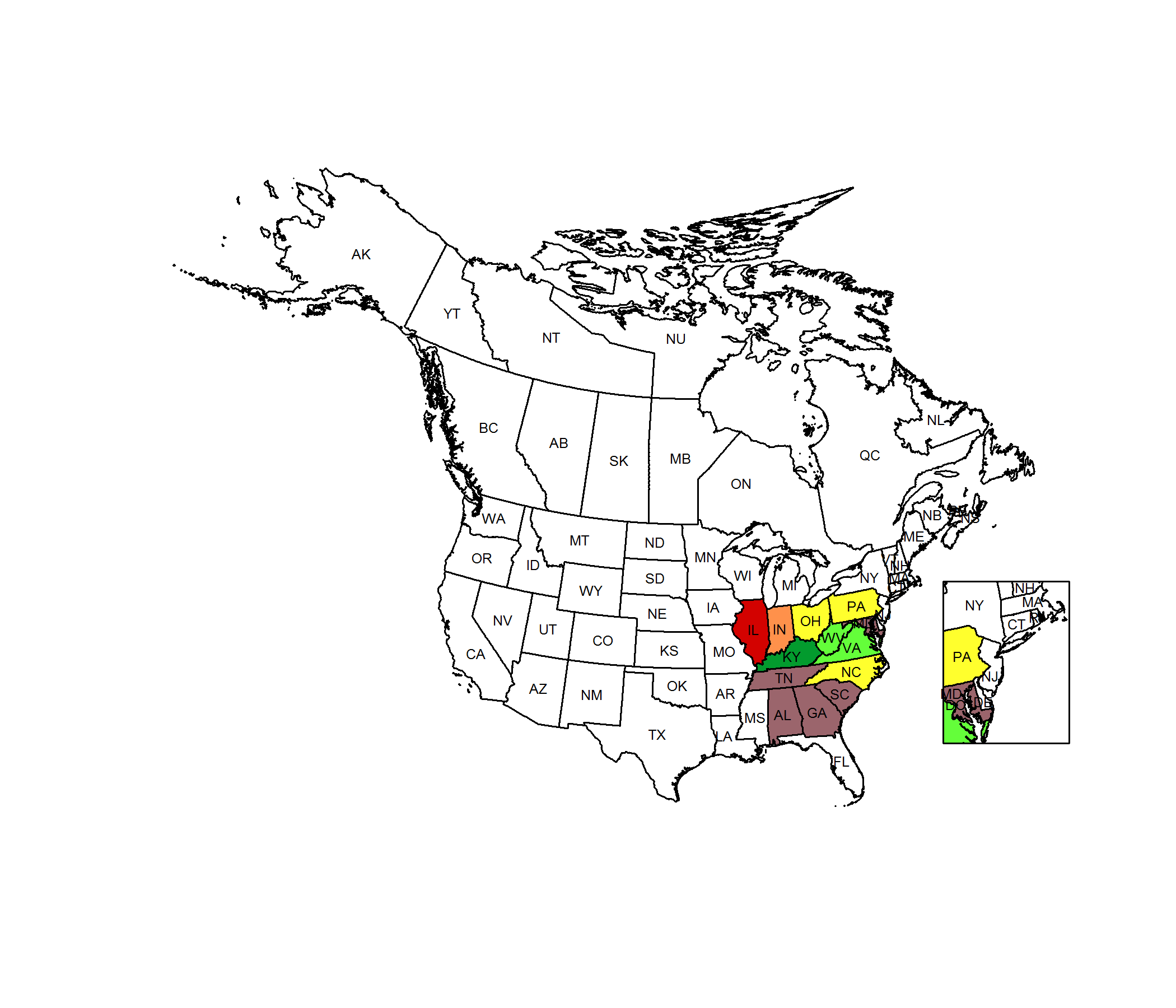
NatureServe. 2017. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available https://explorer.natureserve.org.
https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=peca8
- NatureServe. 2018. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available at https://www.natureserve.org/explorer
- Pennsylvania Natural Heritage Program. 2018.
- Rhoads, A.F. and W.M. Klein, Jr. 1993. The Vascular Flora of Pennsylvania. American Philosophical Society, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Rhoads, A.F. and T.A. Block.
- 2007. The Plants of Pennsylvania: An Illustrated Manual. 2nd edition. University of Pennsylvania Press, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.







